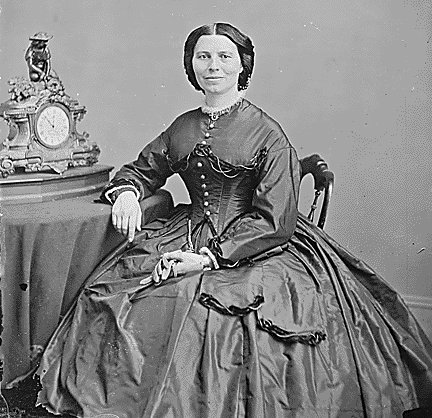
Born on December 25, 1821 in Oxford, Mass., the youngest of 5 children in a middle-class family, Barton was educated at home, and at 15 started teaching school. Her most notable antebellum achievement was the establishment of a free public school in Bordentown, N.J. Though she is remembered as the founder of the American Red Cross, her only prewar medical experience came when for 2 years she nursed an invalid brother.
In 1861 Barton was living in Washington, D.C., working at the U.S. Patent Office. When the 6th Massachusetts Regiment arrived in the city after the Baltimore Riots, she organized a relief program for the soldiers, beginning a lifetime of philanthropy.
When Barton learned that many of the wounded from First Bull Run had suffered, not from want of attention but from need of medical supplies, she advertised for donations in the Worcester, Mass., Spy and began an independent organization to distribute goods. The relief operation was successful, and the following year U.S. Surgeon General William A. Hammond granted her a general pass to travel with army ambulances “for the purpose of distributing comforts for the sick and wounded, and nursing them.”
For 3 years she followed army operations throughout the Virginia theater and in the Charleston, S.C., area. Her work in Fredericksburg, Va., hospitals, caring for the casualties from the Battle of the Wilderness, and nursing work at Bermuda Hundred attracted national notice. At this time she formed her only formal Civil War connection with any organization when she served as superintendent of nurses in Maj. Gen. Benjamin F. Butlers command.
She also expanded her concept of soldier aid, traveling to Camp Parole, Md., to organize a program for locating men listed as missing in action. Through interviews with Federals returning from Southern prisons, she was often able to determine the status of some of the missing and notify families.
By the end of the war Barton had performed most of the services that would later be associated with the American Red Cross, which she founded in 1881. In 1904 she resigned as head of that organization, retiring to her home at Glen Echo, outside Washington, D.C., where she died 12 Apr. 1912.
Source: “Historical Times Encyclopedia of the Civil War” edited by Patricia L. Faust